As RSI indicator for stock trading takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a key tool used in stock trading to identify overbought or oversold conditions, making it essential for traders looking to make informed decisions. In this guide, we will delve into the calculation, interpretation, and practical applications of the RSI indicator to enhance your trading strategies.
Introduction to RSI Indicator
RSI, or Relative Strength Index, is a popular technical indicator used in stock trading to analyze the momentum of price movements. Developed by J. Welles Wilder, RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements, indicating whether a stock is overbought or oversold.
Exploring different options trading strategies can provide investors with alternative ways to profit in the market. Whether utilizing calls, puts, or spreads, understanding how to effectively use options can enhance portfolio flexibility and risk management.
Purpose of RSI in Technical Analysis
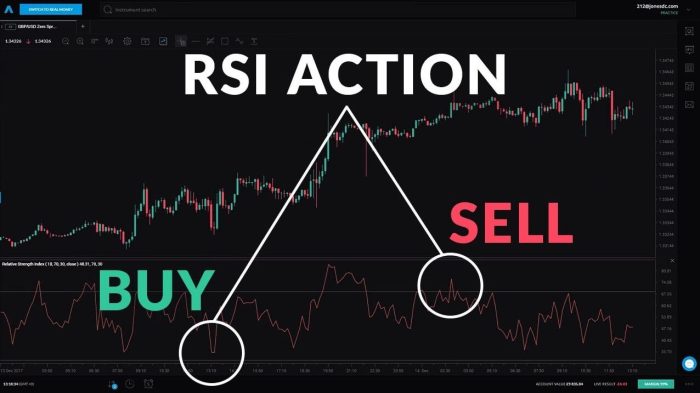
One of the primary purposes of using RSI in technical analysis is to identify potential trend reversals and market extremes. Traders use RSI to determine overbought conditions (when the price is considered too high and may reverse) and oversold conditions (when the price is deemed too low and may bounce back).
By analyzing the RSI values, traders can make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks, depending on whether the RSI indicates a potential reversal or continuation of the current trend.
For those looking to take a more active approach, swing trading explained offers a strategy that focuses on capturing short- to medium-term gains. By analyzing technical indicators and market momentum, swing traders aim to profit from price swings within a specific timeframe.
Calculation and Interpretation of RSI: RSI Indicator For Stock Trading

When it comes to the Relative Strength Index (RSI), understanding how to calculate it and interpret its values is crucial for traders looking to make informed decisions in the stock market.
Formula for Calculating RSI
The RSI is calculated using the following formula:
RSI = 100 – (100 / (1 + RS))
Where RS (Relative Strength) is calculated as the average of x days’ up closes divided by the average of x days’ down closes.
Interpretation of RSI Values
– RSI values above 70 are typically considered overbought, indicating that the stock may be overvalued and due for a potential price correction.
– Conversely, RSI values below 30 are usually seen as oversold, suggesting that the stock may be undervalued and could experience a price increase in the near future.
– Traders often look for divergence between the RSI and stock price movements to identify potential trend reversals or continuation patterns.
Significance of RSI Levels
- RSI at 30: When the RSI falls below 30, it may signal an oversold condition, potentially presenting a buying opportunity for traders expecting a bounce back in the stock price.
- RSI at 70: Conversely, an RSI above 70 could indicate an overbought scenario, prompting traders to consider selling or taking profits as the stock may be due for a pullback.
Using RSI for Divergence Analysis
Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a versatile technical indicator that traders utilize to identify potential trend reversals in the market. RSI divergence analysis is a popular method to predict shifts in price direction based on the relationship between the RSI indicator and the price movements of an asset.
Bullish and Bearish RSI Divergences
When discussing RSI divergences, traders often refer to two main types: bullish and bearish divergences.
- Bullish RSI Divergence: This occurs when the price of an asset makes a lower low, but the RSI indicator forms a higher low. This discrepancy suggests that the current downtrend may be losing momentum and a potential reversal to the upside could be on the horizon.
- Bearish RSI Divergence: On the other hand, bearish RSI divergence happens when the price of an asset forms a higher high, but the RSI indicator creates a lower high. This divergence indicates that the prevailing uptrend might be weakening, signaling a possible downturn in the near future.
Incorporating RSI Divergence into Trading Strategies
Traders can integrate RSI divergence analysis into their trading strategies by using it as a confirmation tool alongside other technical indicators or price action patterns. By waiting for RSI divergences to align with other signals, traders can increase the probability of making successful trades.
When diving into the world of investing, understanding the stock market basics for beginners is crucial. From learning how to buy and sell stocks to grasping the concept of market trends, this knowledge sets a strong foundation for success.
RSI as a Confirmation Tool
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Relative_Strength_Index_RSI_Jul_2020-03-b8781a20e9154a9e9c1e460f298eeabb.jpg?w=700)
When it comes to using the Relative Strength Index (RSI) as a confirmation tool in stock trading, traders rely on this indicator to validate trends identified by other technical analysis tools. This helps to increase the likelihood of making informed trading decisions based on multiple indicators rather than relying solely on one.
Importance of Using RSI in Conjunction with Other Tools
- RSI can provide additional confirmation to signals generated by other indicators, such as moving averages or trend lines. By cross-referencing the signals from different tools, traders can have more confidence in the accuracy of their analysis.
- Using RSI in conjunction with other tools can help traders avoid false signals or traps that may occur when relying on a single indicator. This multi-faceted approach can lead to more reliable trading strategies.
- Combining RSI with other technical analysis tools can provide a more comprehensive view of the market conditions, allowing traders to make more informed decisions based on a holistic analysis of price movements.
RSI Validating Trading Signals
One key aspect of using RSI as a confirmation tool is its ability to validate trading signals generated by other indicators. For example, if a moving average crossover signal indicates a potential trend reversal, traders can look to the RSI to confirm whether the market is indeed overbought or oversold, supporting the validity of the signal.
Setting Up RSI on Trading Platforms
To start using the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator on popular trading platforms, you will need to follow a few simple steps. Adding RSI to your trading platform can help you make informed decisions based on market trends and price movements.
Adding RSI Indicator
- For MetaTrader 4 (MT4): Click on ‘Insert’ in the top menu, then navigate to ‘Indicators’ and select ‘Oscillators’. Choose ‘Relative Strength Index (RSI)’ from the list.
- For TradingView: Go to the ‘Indicators’ tab, search for ‘RSI’, and click on it to add it to your chart.
- For Thinkorswim: Click on the ‘Studies’ tab, search for ‘Relative Strength Index’, and then click ‘Add selected’ to apply it to your chart.
Customization Options, RSI indicator for stock trading
- Period: Adjust the number of periods used to calculate RSI (usually set at 14 by default).
- Overbought and Oversold Levels: Modify the levels at which RSI indicates overbought or oversold conditions (typically set at 70 and 30).
- Colors and Line Styles: Customize the appearance of the RSI line on the chart for better visibility.
Adjusting RSI Settings
Traders can tweak RSI settings based on their trading style and preferences. For example, short-term traders may prefer a lower period setting for more sensitive readings, while long-term investors might opt for a higher period for smoother signals.
Best Practices and Tips for RSI Trading
When utilizing the Relative Strength Index (RSI) in stock trading, it is essential to follow best practices and implement effective strategies to maximize its potential. Below are some common mistakes to avoid, tips for using RSI in various market conditions, and strategies for combining RSI with other technical indicators for better trading decisions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Avoid relying solely on RSI for trading decisions. It is essential to consider other factors and indicators for a comprehensive analysis.
- Avoid using RSI in isolation without confirmation from other technical tools or price action signals.
- Avoid chasing overbought or oversold signals blindly without considering the overall market context.
- Avoid ignoring the trend direction when interpreting RSI readings, as it can provide valuable insights.
Tips for Effectively Using RSI
- Combine RSI with trend analysis to confirm signals and avoid false alarms.
- Adjust the RSI period based on the trading timeframe to adapt to different market conditions.
- Use RSI divergence to anticipate potential reversals or trend changes in the stock price.
- Consider using RSI in conjunction with other momentum indicators for a more robust trading strategy.
Strategies for Combining RSI with Other Indicators
- Combine RSI with moving averages to identify potential entry and exit points in the market.
- Use RSI in conjunction with volume analysis to confirm the strength of a price move.
- Employ RSI alongside support and resistance levels to validate trading signals and manage risk effectively.
- Consider integrating RSI with Fibonacci retracement levels for precise price target identification.
In conclusion, the RSI indicator stands out as a versatile tool for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of the stock market. By understanding how to effectively use RSI in conjunction with other indicators and incorporating best practices, you can elevate your trading game and achieve success in your investment endeavors.