How to analyze stock charts: Dive into the world of stock analysis with this comprehensive guide that explores the intricacies of interpreting stock charts and patterns, technical indicators, and volume trends.
Stock charts are a vital tool for investors, providing crucial insights into market trends and potential price movements. By understanding the components of stock charts, reading patterns, analyzing technical indicators, and interpreting volume trends, investors can make informed decisions to navigate the ever-changing stock market landscape.
Understanding Stock Charts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Introductio_to_Technical_Analysis_Price_Patterns_Sep_2020-05-a19b59070c434400988fca7fa83898dd.jpg?w=700)
Stock charts are visual representations of a stock’s price movement over a specific period of time. They are essential tools for investors to analyze market trends and make informed decisions based on historical price data.
When it comes to stock trading, one popular strategy that many traders use is scalping. This short-term trading technique involves making quick trades to profit from small price movements. On the other hand, investors who prefer a more long-term approach may be interested in understanding the differences between value investing and growth investing. Value investors look for undervalued stocks with strong fundamentals, while growth investors focus on companies with high growth potential.
For beginners looking to enter the stock market, it’s essential to learn the basics before making any investment decisions.
Components of a Stock Chart
- The x-axis represents time, with each point on the chart corresponding to a specific date or time period.
- The y-axis represents the stock price, showing the value of the stock at a particular point in time.
- Stock charts may also include other elements such as volume bars, moving averages, and technical indicators.
Importance of Stock Charts
Stock charts play a crucial role in analyzing market trends, identifying patterns, and predicting future price movements. They help investors understand the historical performance of a stock and make well-informed decisions.
When it comes to stock trading, one of the popular strategies used by traders is scalping. This involves making quick trades to profit from small price movements. On the other hand, investors often debate between value investing and growth investing. Value investors look for undervalued stocks, while growth investors focus on companies with potential for high growth.
For beginners looking to enter the stock market, understanding the basics is crucial for success.
Types of Stock Charts
- Line Charts: Show the closing prices of a stock over a specific period, connecting each data point with a line.
- Candlestick Charts: Provide more detailed information, showing the open, high, low, and close prices of a stock for each time period.
- Bar Charts: Display the price range for a stock within a specific time frame, with a vertical line indicating the high and low prices.
Reading Stock Chart Patterns

When analyzing stock charts, it’s essential to identify key patterns that can provide insights into potential price movements. Understanding patterns such as head and shoulders, double tops/bottoms, triangles, and flags can help traders make informed decisions based on technical analysis.
Head and Shoulders Pattern
The head and shoulders pattern is a reversal pattern that indicates a potential change in trend. It consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being higher than the other two (the shoulders). A break below the “neckline” drawn through the lows of the pattern suggests a bearish reversal.
Double Tops/Bottoms
Double tops and bottoms are also reversal patterns that indicate a potential change in trend. A double top forms after an uptrend and signals a bearish reversal, while a double bottom forms after a downtrend and signals a bullish reversal. Traders look for a break below the “neckline” in double tops and a break above the “neckline” in double bottoms to confirm the pattern.
Triangles
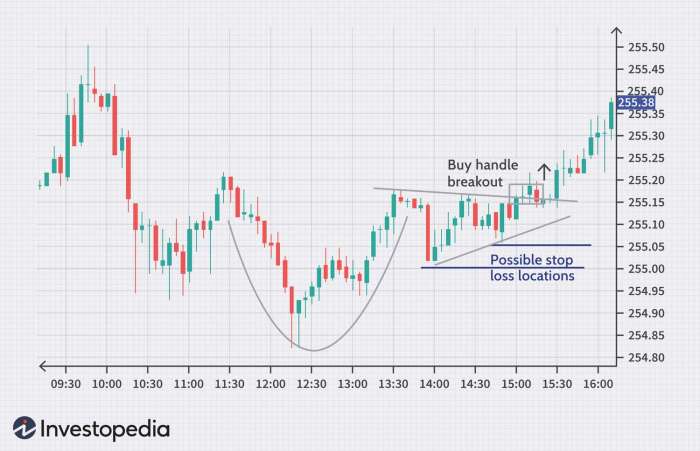
Triangles are continuation patterns that signal a pause in the current trend before resuming. There are three main types of triangles: symmetrical, ascending, and descending. A breakout from the triangle pattern can indicate the direction of the next price movement.
Flags
Flags are short-term continuation patterns that represent a brief pause in the trend before continuing in the same direction. A bullish flag is a small consolidation after an upward price movement, while a bearish flag is a small consolidation after a downward price movement. Traders watch for a breakout from the flag pattern to confirm the continuation of the trend.
By recognizing and interpreting these key chart patterns, traders can gain valuable insights into potential price movements and make more informed trading decisions.
Technical Indicators on Stock Charts
Technical indicators play a crucial role in analyzing stock charts as they provide valuable insights into the market trends and potential buy/sell signals. These indicators are based on mathematical calculations applied to historical price data, helping traders make informed decisions.
Moving Averages
Moving averages smooth out price data over a specific period, showing the average price over time. They help identify trends by highlighting the direction in which a stock is moving. For example, a moving average crossover, where a short-term moving average crosses above a long-term moving average, can signal a potential trend reversal.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price. It consists of a MACD line and a signal line, with crossovers between the two lines indicating potential buy or sell signals. Traders use MACD to confirm trends and identify entry/exit points.
RSI (Relative Strength Index)
RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It ranges from 0 to 100 and is used to determine overbought or oversold conditions in a stock. An RSI above 70 indicates overbought territory, while an RSI below 30 indicates oversold territory. Traders can look for potential reversal signals based on RSI levels.
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of a middle band (usually a 20-day moving average) and two outer bands representing standard deviations of the middle band. These bands expand and contract based on market volatility. When the price moves close to the upper band, it may indicate overbought conditions, while a move towards the lower band may signal oversold conditions.
Combining Technical Indicators
Traders often use a combination of technical indicators to enhance the accuracy of their analysis. For example, combining moving averages with RSI can help confirm trends identified by moving averages and pinpoint potential entry points based on RSI signals. It’s essential to use multiple indicators to validate signals and reduce false alarms.
Analyzing Volume and Price Trends: How To Analyze Stock Charts

When analyzing stock charts, understanding the relationship between volume and price movements is crucial. Volume refers to the number of shares being traded, while price movements indicate the direction in which the stock price is moving. The interplay between volume and price trends can provide valuable insights into the strength of a particular trend or potential reversals in the market.
Relationship Between Volume and Price Movements, How to analyze stock charts
- High volume accompanied by price increases typically indicates a strong bullish trend, suggesting that there is significant buying interest in the stock.
- Conversely, if the price is falling on high volume, it may signal a bearish trend, with selling pressure outweighing buying interest.
- Low volume during price movements can suggest a lack of conviction in the market and may indicate a period of consolidation or indecision among investors.
Changes in Volume Validating or Invalidating Price Trends
- When a stock price is moving in a particular direction and volume increases, it can validate the strength of the trend, confirming that there is substantial market participation supporting the price movement.
- If a stock price is rising, but volume is decreasing, it may indicate weakening momentum and a potential reversal in the trend, as the lack of volume support could lead to the price being unsustainable.
Significance of Volume Spikes or Divergences
- Volume spikes, where there is a sudden and substantial increase in trading volume, can signal significant market interest and potential for a strong price movement in the direction of the spike.
- Divergences between price and volume trends, where the price is moving in one direction while volume is moving in the opposite direction, can indicate underlying weakness or strength in the market that may lead to trend reversals.
- Monitoring volume spikes and divergences can help traders and investors anticipate potential changes in price trends and make informed decisions based on market sentiment and participation.
In conclusion, mastering the art of analyzing stock charts is essential for any investor looking to succeed in the dynamic world of stock trading. By combining technical analysis with a deep understanding of market trends, investors can gain a competitive edge and make well-informed investment decisions.