What is a REIT? This intriguing investment vehicle known as a Real Estate Investment Trust has been gaining popularity in the financial world. Let’s dive into the details to uncover what makes REITs unique and attractive to investors.
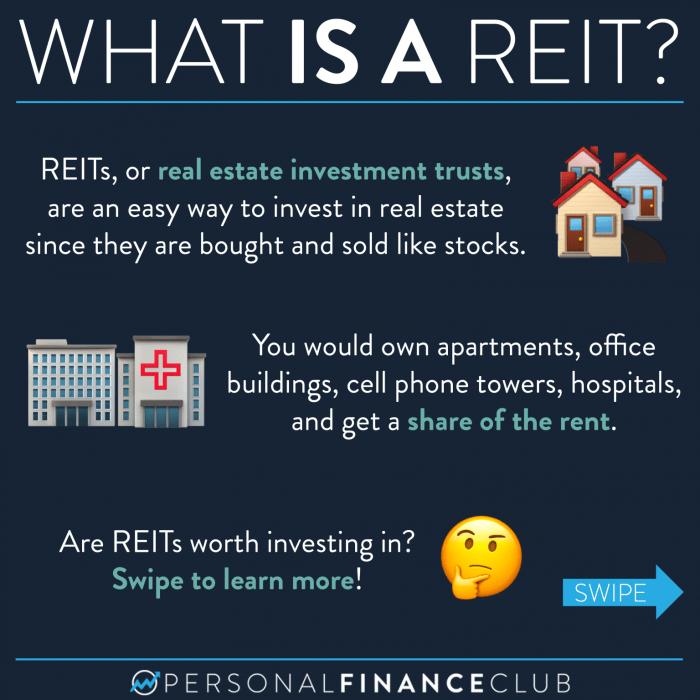
What is a REIT?

A Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) is a company that owns, operates, or finances income-producing real estate across a range of property sectors. REITs provide investors with the opportunity to invest in real estate without having to buy or manage properties directly.
When it comes to investing in rental properties, it’s crucial to understand how to calculate cash flow. This involves analyzing expenses, rental income, and potential vacancies. By utilizing a detailed formula, investors can determine their cash flow and make informed decisions. To learn more about how to calculate cash flow on rental properties , visit our comprehensive guide.
Types of REITs, What is a REIT?
There are several types of REITs available to investors:
- Equity REITs: These REITs own and operate income-producing real estate properties. They generate revenue mainly through rental income.
- Mortgage REITs: Mortgage REITs provide financing for income-producing real estate by purchasing or originating mortgages and mortgage-backed securities.
- Hybrid REITs: Hybrid REITs combine both the characteristics of Equity REITs and Mortgage REITs, owning properties while also providing financing.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
Investing in REITs offers several advantages compared to other real estate investments:
- Diversification: REITs provide exposure to a diversified portfolio of real estate assets, reducing risk compared to investing in individual properties.
- Liquidity: REITs are traded on major stock exchanges, offering liquidity to investors who can easily buy and sell shares.
- Dividend Income: REITs are required to distribute a significant portion of their income to shareholders in the form of dividends, providing a steady income stream.
- Tax Benefits: REITs are pass-through entities that do not pay corporate income tax if they distribute at least 90% of their taxable income to shareholders, resulting in potentially higher dividend yields.
Types of REITs
When it comes to Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), there are several categories that investors can consider. These categories include equity REITs, mortgage REITs, and hybrid REITs, each with its own unique investment focus and characteristics.
Equity REITs
Equity REITs are the most common type of REITs and invest in income-producing real estate properties. These properties can include commercial buildings, residential apartments, shopping centers, and more. Equity REITs generate revenue primarily through renting out these properties and collecting rental income from tenants. A successful example of an equity REIT is Simon Property Group, Inc., which focuses on owning and operating shopping malls and premium outlets across the United States.
Mortgage REITs
On the other hand, mortgage REITs do not own physical real estate properties. Instead, they provide financing for real estate by investing in mortgages and mortgage-backed securities. Mortgage REITs make money through the interest earned on these investments. An example of a successful mortgage REIT is Annaly Capital Management, Inc., which focuses on investing in residential and commercial mortgage-backed securities.
Hybrid REITs
Hybrid REITs combine features of both equity and mortgage REITs, diversifying their portfolios by investing in both real estate properties and mortgages. This allows them to benefit from both rental income and interest payments. A notable example of a hybrid REIT is Realty Income Corporation, which owns a portfolio of commercial properties and has a history of consistent dividend payments to investors.
Market conditions can have a significant impact on different types of REITs. For example, equity REITs may benefit from a strong real estate market with high demand for rental properties, while mortgage REITs may face challenges in a rising interest rate environment. It is essential for investors to understand the unique characteristics of each type of REIT and consider how market conditions can affect their investments.
How to Invest in REITs

Investing in REITs can be a lucrative way to diversify your portfolio and generate passive income. Here are the steps involved in investing in REITs and some tips for beginners looking to get started.
Steps to Invest in REITs
- Do your research: Before investing in any REIT, make sure to research the company’s financial health, management team, and property portfolio.
- Choose a brokerage account: You will need a brokerage account to buy and sell REITs. Make sure to choose a reputable broker with low fees.
- Select the type of REIT: Decide whether you want to invest in equity REITs, mortgage REITs, or hybrid REITs based on your investment goals.
- Buy REIT shares: Once you have done your research and chosen a REIT, you can buy shares through your brokerage account.
- Monitor your investment: Keep track of your REIT investment’s performance and make adjustments as needed to optimize your portfolio.
Risks Associated with Investing in REITs
- Interest rate risk: REITs are sensitive to changes in interest rates, which can affect their profitability and stock prices.
- Market risk: Like any other investment, REITs are subject to market fluctuations that can impact their value.
- Liquidity risk: Some REITs may have lower trading volumes, making it difficult to sell shares quickly at a fair price.
Individual REITs vs. REIT Mutual Funds or ETFs
- Investing in individual REITs gives you more control over your investments but requires more research and monitoring.
- REIT mutual funds or ETFs offer diversification and professional management but come with management fees.
- Consider your investment goals and risk tolerance when deciding between individual REITs and REIT funds.
Tips for Beginners
- Start small: Begin with a modest investment in a REIT to get a feel for how they perform in your portfolio.
- Diversify: Spread your investments across different types of REITs to minimize risk and maximize returns.
- Stay informed: Keep up to date with market trends and news that may impact the real estate sector and your REIT investments.
REIT Performance Metrics: What Is A REIT?

When evaluating Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), investors rely on key performance metrics to assess the financial health and performance of these entities. Understanding metrics such as Funds from Operations (FFO), Dividend Yield, and Price-to-Funds from Operations (P/FFO) ratio is crucial in making informed investment decisions.
Funds from Operations (FFO)
Funds from Operations (FFO) is a vital metric for REITs as it provides a clearer picture of the operating performance by excluding the effects of depreciation and gains or losses from sales of properties. FFO is calculated by adding depreciation and amortization to earnings and subtracting gains on sales of properties.
Dividend Yield
Dividend Yield is another important metric that measures the annual dividend income as a percentage of the REIT’s stock price. It indicates the return on investment through dividends and is a key factor for income-oriented investors. A higher dividend yield can be attractive, but investors should also consider sustainability and growth potential.
Price-to-Funds from Operations (P/FFO) Ratio
The Price-to-Funds from Operations (P/FFO) ratio is used to evaluate the valuation of a REIT by comparing its stock price to its FFO per share. A lower P/FFO ratio may indicate that a REIT is undervalued, while a higher ratio may suggest overvaluation. Investors use this ratio to assess whether a REIT’s stock price is justified based on its earnings.
Impact of External Factors
External factors such as interest rates can significantly influence REIT performance metrics. For example, when interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing for REITs increases, affecting their profitability and potentially reducing FFO. This can lead to a decrease in dividend yield and impact the valuation of REITs, reflected in the P/FFO ratio.
In conclusion, understanding the ins and outs of REITs can open up a world of opportunities for investors looking to diversify their portfolios with real estate assets. Dive in and explore the potential of REIT investments today.
Investing in rental properties can be a lucrative venture if approached strategically. Understanding market trends, property management, and financial planning are essential for success in this industry. For those looking to start or expand their rental property portfolio, investing in rental properties can provide long-term benefits and passive income streams.
One of the key factors in investing in rental properties is knowing how to finance them effectively. Whether through traditional mortgages, loans, or partnerships, finding the right financing option is crucial for a successful investment. To explore various strategies on how to finance a rental property , check out our expert advice.